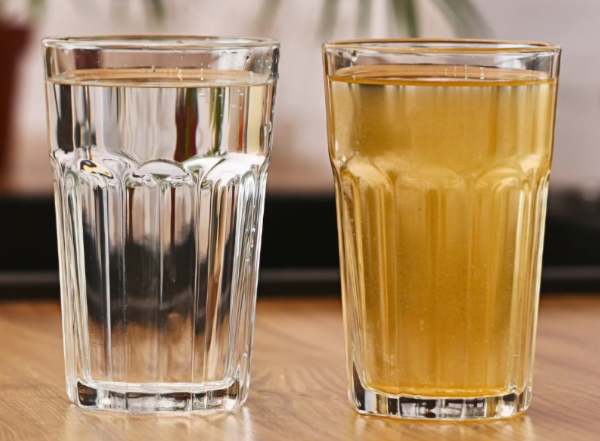
How to Treat Reddish-Yellow Well Water
- Sudarma Linggih, Ir. MBA
- Apr 22
- 3 min read
Well water that appears reddish-yellow usually indicates a high concentration of iron (Fe) or manganese (Mn), and may even be due to the presence of coliform bacteria.
Causes of the Reddish-Yellow Color:
1. Iron (Fe²⁺/Fe³⁺):
When water is pumped from underground, Fe²⁺ (ferrous iron) oxidizes upon contact with air into Fe³⁺ (ferric iron), forming reddish-brown iron oxide precipitates (Fe(OH)₃). This causes the water to appear yellowish-brown or rusty red.
2. Manganese (Mn²⁺):
Even in small amounts, manganese can cause the water to turn dark gray or black after exposure to air.
3. Shallow groundwater or wells located near peatland or laterite soils (rich in iron) can also be sources of this discoloration.
Additionally, the well might not be sealed properly and could be located near a septic tank. Or, the well site may be unprotected from rainwater runoff and not tightly covered.
4. The presence of coliform and E. coli indicates fecal contamination, which is dangerous even if the water appears clear. A few days later, the water may turn cloudy.
Chemical and Physical Conditions of that kind of water are :

The general physical and chemical condition of such water usually does not meet the standards set by the Ministry of Health regulation, PERMENKES No. 2 of 2023, Republic of Indonesia, for MCK water (bathing, washing, and toilet use)—especially if the water is also used for brushing teeth or washing hands.

PERMENKES No.2 of 2023 Standards (for MCK Water):
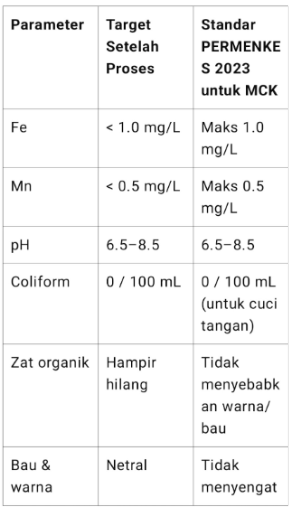
pH: 6.5–8.5
Fe (Iron): ≤ 1.0 mg/L (for MCK)
Mn (Manganese): ≤ 0.5 mg/L
TDS: ≤ 1000 mg/L
Total coliform: none detected in 100 ml (especially if used for brushing teeth or washing hands).
To overcome the above water conditions, a combination of filtration and oxidation can be applied before storing the water in a tank or reservoir.
Several alternatives for water filtering and purification system are as follows:
1. Filtration of Iron and Manganese Content & Reduction of Turbidity:
Iron and manganese content are generally removed using oxidative filter media, such as: Manganese greensand (or Birm media, Ferrolite, etc.) which is combined with silica sand (particle size 0.4 – 0.8 mm).
These can be housed in a single filter tank or in separate tanks.
2. Purification and Reduction of Organic Content with Activated Carbon Filter Media:
Activated carbon media is highly effective in removing odor and organic compounds
However, this media needs regular replacement every 1 to 1.5 years as it becomes saturated after absorbing organics over time.
3. Oxidation and Disinfection Equipment to Eliminate Coliform Bacteria and Organic Content:
UV sterilizer (optional, for killing bacteria)
Oxidation using ozone and EAOP (Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Process).
Light chlorination using bleaching powder (calcium hypochlorite / chlorine) is sometimes used, but this method is less eco-friendly and not ideal for health
4. For Large-Scale Filtration Systems –
(e.g., for hotels, resorts, or apartments)--,
an oxygen injection device such as an aerator, venturi injector, etc., is often added before the water enters the silica and manganese zeolite filters to increase oxidation efficiency and effectiveness.
Aeration + Sedimentation:
oxidation of Fe²⁺ → Fe³⁺
With the filtration system as described above, the desired outcome is for the well water to meet the standards of PERMENKES No.2 of 2023 and to be clear and suitable for MCK needs (bathing, washing, and toilet use).
Water Quality Target & and Standard :
CONCLUSION:
In summary, the general process flow of the water filtration system to treat reddish-yellow well water that becomes cloudy after exposure to air (containing 20% oxygen) is as follows:
Well Water → Pump → Manganese Zeolite and Silica Sand Filter (optional: Aeration) → Activated Carbon → Water Disinfection/Oxidation Unit (Ozone, UV Lamp, EAOP, or Chlorine).
Attachment:
Image of manganese zeolite, silica sand and activated carbon.






Comments